Background Introduction
Industrial PCs (IPCs) are the backbone of industrial automation and control systems, designed to deliver high performance and reliability in harsh environments. Understanding their core components is essential for selecting the right system to meet specific application requirements. In this first part, we will explore the foundational components of IPCs, including the processor, graphics unit, memory, and storage systems.
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is often regarded as the brain of the IPC. It executes instructions and performs calculations required for various industrial processes. Choosing the right CPU is critical because it directly impacts the performance, power efficiency, and suitability for specific applications.
Key Features of IPC CPUs:
- Industrial Grade: IPCs typically use industrial-grade CPUs with extended lifecycles, offering long-term reliability in harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures and vibrations.
- Multi-Core Support: Modern IPCs often feature multi-core processors to enable parallel processing, essential for multitasking environments.
- Energy Efficiency: CPUs like Intel Atom, Celeron, and ARM processors are optimized for low power consumption, making them ideal for fanless and compact IPCs.
Examples:
- Intel Core Series (i3, i5, i7): Suitable for high-performance tasks such as machine vision, robotics, and AI applications.
- Intel Atom or ARM-Based CPUs: Ideal for basic data logging, IoT, and lightweight control systems.
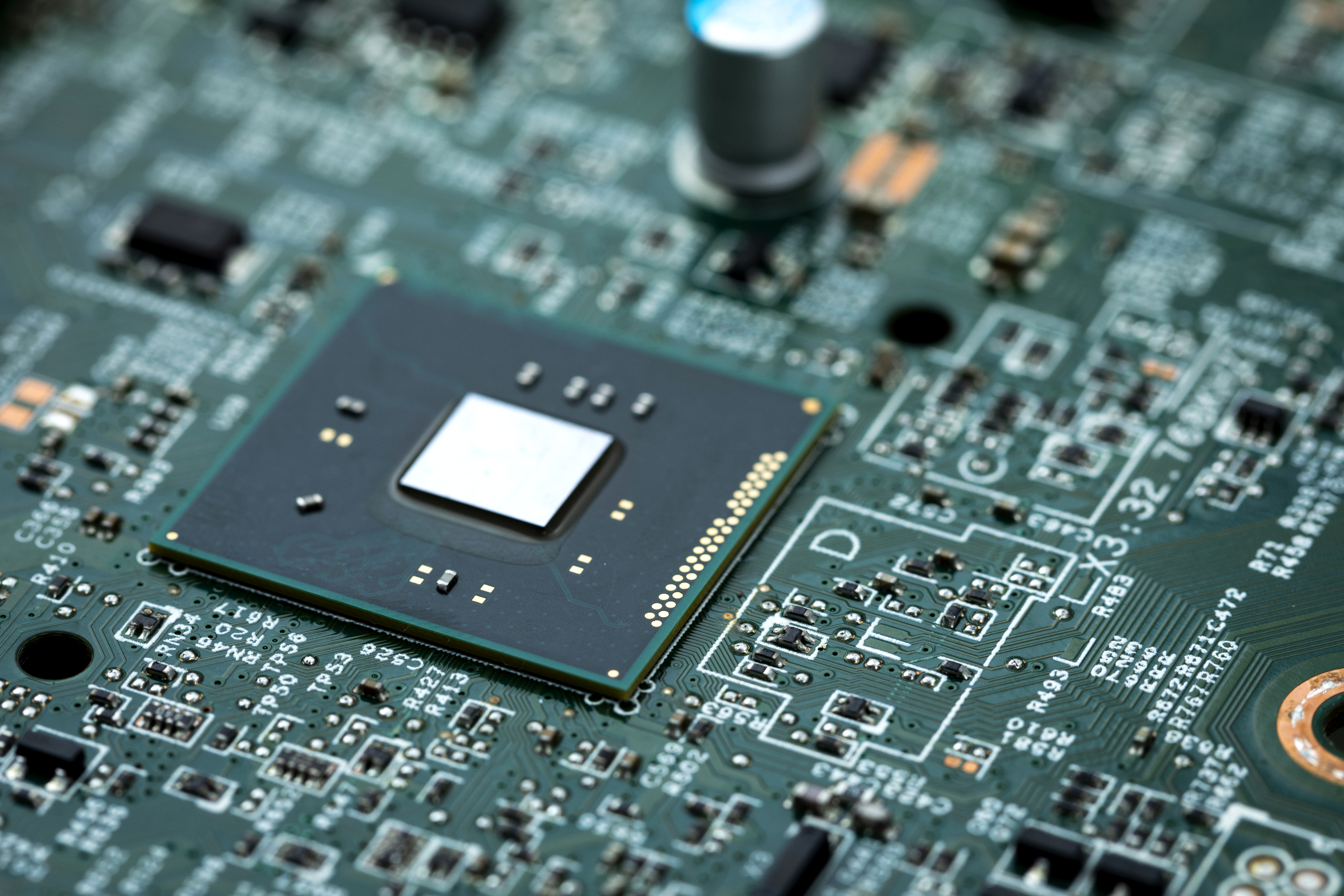
2. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
The GPU is a crucial component for tasks that require intensive visual processing, such as machine vision, AI inference, or graphical data representation. IPCs can either use integrated GPUs or dedicated GPUs depending on the workload.
Integrated GPUs:
- Found in most entry-level IPCs, integrated GPUs (e.g., Intel UHD Graphics) are sufficient for tasks like 2D rendering, basic visualization, and HMI interfaces.
Dedicated GPUs:
- High-performance applications like AI and 3D modeling often require dedicated GPUs, such as NVIDIA RTX or Jetson series, to handle parallel processing for large datasets.
Key Considerations:
- Video Output: Ensure compatibility with display standards such as HDMI, DisplayPort, or LVDS.
- Thermal Management: High-performance GPUs may require active cooling to prevent overheating.

3. Memory (RAM)
RAM determines how much data an IPC can process simultaneously, directly affecting system speed and responsiveness. Industrial PCs often use high-quality, error-correcting code (ECC) RAM for enhanced reliability.
Key Features of RAM in IPCs:
- ECC Support: ECC RAM detects and corrects memory errors, ensuring data integrity in critical systems.
- Capacity: Applications like machine learning and AI may require 16GB or more, while basic monitoring systems can function with 4–8GB.
- Industrial Grade: Designed to withstand temperature extremes and vibrations, industrial-grade RAM offers higher durability.
Recommendations:
- 4–8GB: Suitable for lightweight tasks such as HMI and data acquisition.
- 16–32GB: Ideal for AI, simulation, or large-scale data analysis.
- 64GB+: Reserved for highly demanding tasks like real-time video processing or complex simulations.

4. Storage Systems
Reliable storage is essential for IPCs, as they often operate continuously in environments with limited maintenance access. Two main types of storage are used in IPCs: solid-state drives (SSDs) and hard disk drives (HDDs).
Solid-State Drives (SSDs):
- Preferred in IPCs for their speed, durability, and resistance to shocks.
- NVMe SSDs provide higher read/write speeds compared to SATA SSDs, making them suitable for data-intensive applications.
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs):
- Used in scenarios where high storage capacity is required, though they are less durable than SSDs.
- Often combined with SSDs in hybrid storage setups to balance speed and capacity.
Key Features to Consider:
- Temperature Tolerance: Industrial-grade drives can operate in a wider temperature range (-40°C to 85°C).
- Longevity: High endurance drives are crucial for systems with frequent write cycles.

5. Motherboard
The motherboard is the central hub that connects all components of the IPC, facilitating communication between the CPU, GPU, memory, and storage.
Key Features of Industrial Motherboards:
- Robust Design: Built with conformal coatings to protect against dust, moisture, and corrosion.
- I/O Interfaces: Include a variety of ports such as USB, RS232/RS485, and Ethernet for connectivity.
- Expandability: PCIe slots, mini PCIe, and M.2 interfaces allow for future upgrades and additional functionality.
Recommendations:
- Look for motherboards with industrial certifications like CE and FCC.
- Ensure compatibility with required peripherals and sensors.

The CPU, GPU, memory, storage, and motherboard form the foundational building blocks of an industrial PC. Each component must be carefully chosen based on the application’s performance, durability, and connectivity requirements. In the next part, we will delve deeper into additional critical components such as power supplies, cooling systems, enclosures, and communication interfaces that complete the design of a reliable IPC.
If you're interested in our company and products, feel free to contact our overseas representative, Robin.
Email: yang.chen@apuqi.com
WhatsApp: +86 18351628738
Post time: Jan-03-2025

